Identify the Two Types of Capillaries With a Complete Endothelium
Capillaries are of three types- Continuous Fenestrated and Sinusoidal capillaries. Which capillaries have wide intercellular pores that serve as a basement membrane over the capillary endothelium for increased filtration.
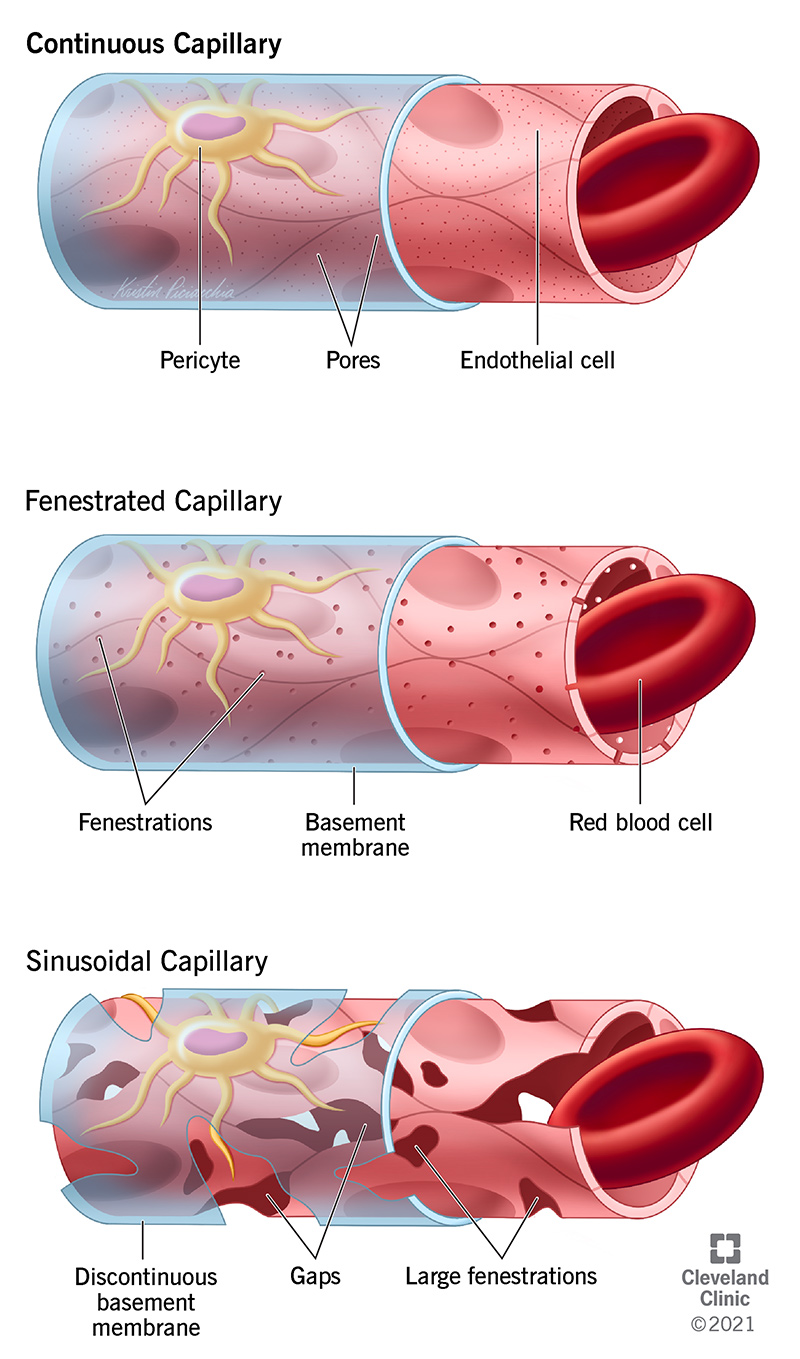
Continuous Capillaries Anatomy And Function
The most common type of capillary the continuous capillary is found in almost all vascularized tissues.

. Sometimes a single endothelial cell makes up the entire circumference of the wall of the capillary. Two types of pressure interact to drive each of these movements. There are three types of capillaries which include.
Figure 205 Types of Capillaries The three major types of capillaries. Distribution of body water between intravascular and interstitial fluid compartments. Brain Tumors Third Edition 2012.
Continuous Capillaries The most common type of capillary the continuous capillary is found in almost all vascularized tissues. Asked Sep 27 2015 in Anatomy Physiology by Karlena. At what sites in the body are fenestrated capillaries located.
Continuous capillaries can also be found in the lungs and various fat and muscle tissues and both the endothelium and basal lamina or the area where the endothelium sits are continuous. Asked Sep 4. In contrast to arteries and veins the capillary wall is almost entirely composed of endothelium and is only one cell thick supported by a basement membrane.
Continuous capillaries are characterized by a complete endothelial lining with tight junctions between. As their name suggests continuous capillaries have a continuous endothelial lining. Capillary endothelial cells in metastatic brain tumors display characteristics found in blood vessels of systemic neoplasms including gap junctions and membrane fenestration with these characteristics being most common in the center of the tumor Long 1979.
The endothelium of the glomerulus is made up of _________ capillaries. Identify the two types of capillaries with a complete endothelium. There are three major types of capillaries which differ according to their degree of leakiness continuous fenestrated and sinusoid capillaries.
Most of the body is supplied with continuous capillaries. Hydrostatic Pressure The primary force driving fluid transport between the capillaries and tissues is hydrostatic pressure which can be defined as the pressure of any fluid enclosed in a space. These make the capillary permeable to larger molecules.
They contain small gaps in between their endothelial cells that allow for things like gases water sugar glucose and some hormones to pass through. Module 193A A continuous capillaries and fenestrated capillaries B fenestrated capillaries and sinusoidal capillaries C continuous capillaries and sinusoidal capillaries D fenestrated capillaries and lacteals E sinusoidal capillaries and collaterals. These capillaries also have pinocytotic vesicles and fine filaments.
Kidneys small intestine Organs that require rapid absorption or filtration Endothelial cells riddled with holes called filtration pores fenestrations Spanned by very thin glycoprotein layer Allows passage of only small molecules. Asked Oct 27 2021 in Anatomy Physiology by harsh23. These capillaries have small pores that allow small molecules through and are located in the intestines kidneys and endocrine glands.
They have tight junctions between their endothelial cells along with intercellular clefts through which small molecules like ions can pass. The pulmonary circulation should be viewed as a series of networks from arteries to capillaries and veins. Continuous fenestrated and sinusoid.
Perivascular cells - peri is greek for around lie just underneath the endothelium of blood capillaries and are a source of new fibroblasts. Continuous fenestrated and sinusoidal. Choroid plexus of the brain capillaries of the hypothalamus pituitary gland pineal gland and thyroid gland.
231 Whereas pulmonary artery endothelial cells are. Asked Jul 27 2018 in Anatomy Physiology by J_Alexander. Continuous capillary and fenestrated capillary.
Continuous fenestrated and sinusoid. These are the most common type of capillary in the body. Of the various types of connective tissue which type can be.
Types of capillaries. There are three types of capillary. They are present in the bone marrow lymph nodes and the spleen and are in.
We identified two endothelial cell clusters as capillaries based on expression of carbonic anhydrases Car4 Car14 that catalyze the conversion of bicarbonate to carbon dioxide 41 Gpihbp1 a lipoprotein binding protein that localizes to the luminal membrane of alveolar capillaries 42 and lipoprotein lipase Lpl which is transported to the capillary lumen by. Figure 205 Types of Capillaries The three major types of capillaries. Hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure.
They are also called non-fenestrated capillaries. The most common type of capillary the continuous capillary is found in almost all vascularized tissues. In continuous capillaries the endothelium forms a complete lining.
These capillaries have large open poreslarge enough to allow a blood cell through. Identify the two types of capillaries with a complete endothelium. The ____ is composed of endothelium and is continuous with the endocardium of hte heart.
Continuous capillaries are characterized by a complete endothelial lining with tight. A fenestrated capillary is one that has pores or fenestrations in addition to tight junctions in the endothelial lining. Types of Capillaries Three types of capillaries cont Fenestrated capillaries.
There are three major types of capillaries which differ according to their degree of leakiness continuous fenestrated and sinusoid capillaries. Continuous capillaries are generally found in the nervous system as well as in fat and. This classification is done according to the size of gaps between the endothelial cells of the capillaries.
There are three major types of capillaries which differ according to their degree of leakiness continuous fenestrated and sinusoid capillaries Figure 2014. Delivery of nutrients to and removal of metabolites from the tissues. Capillaries have two main roles.
These are the most common types of capillaries. Continuous capillaries often have pericytes associated with them. Fenestrated Capillaries A fenestrated capillary is one that has pores or fenestrations in addition to tight junctions in the endothelial lining.
The endothelium in each of these vessels displays unique characteristics and endothelial phenotypes vary distinctly in terms of origin morphology and function along the length of the pulmonary circulation. 181 Identify the two types of capillaries with a complete endothelium.

Structure And Function Of Blood Vessels Anatomy And Physiology Ii
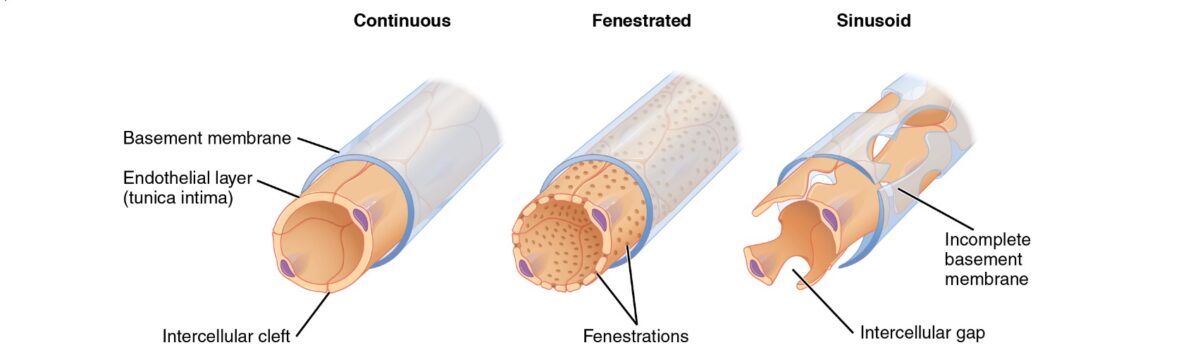
Capillaries Histology Concise Medical Knowledge
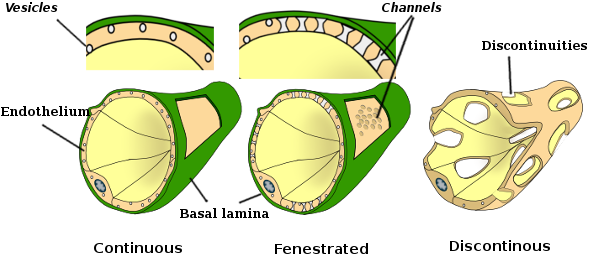
Cell Types Endothelial Cell Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology
No comments for "Identify the Two Types of Capillaries With a Complete Endothelium"
Post a Comment